We have made a final decision on the maximum prices exempt sellers may charge embedded network customers.
Maximum electricity prices for embedded networks and other exempt sellers review 2020
- Consultation paper11 February 2020
- Draft decision6 May 2020
- Public forum (online)28 May 2020
- Submissions to our draft decision close15 June 2020
- Final decision28 July 2020
- New prices are implemented1 September 2020
Overview
We have made our final decision on the maximum prices exempt sellers may charge customers in embedded networks.
From 1 September 2020, Victorian Default Offer prices will be the new maximum prices for all households and most businesses in embedded networks.
Residential embedded network customers could save between $180 to $360 while small businesses could save $900 to $2200 annually. Estimated savings are based on an assessment of the expected impact of the current Victorian Default Offer on standing offer prices as of May 2019.
Our final decision
Our final decision is that the maximum price for residential and small business customers (consuming less than 40 megawatt hours of electricity per year) within embedded networks will be set at the level of the Victorian Default Offer, covering most embedded network customers.
For a relatively small group of customers (including large businesses), we have not made a decision on prices. For these customers prices will remain at current levels - our final decision explains why.
New maximum prices apply from 1 September 2020.
Maximum prices for exempt sellers will automatically update to align with pricing resets for the Victorian Default Offer.
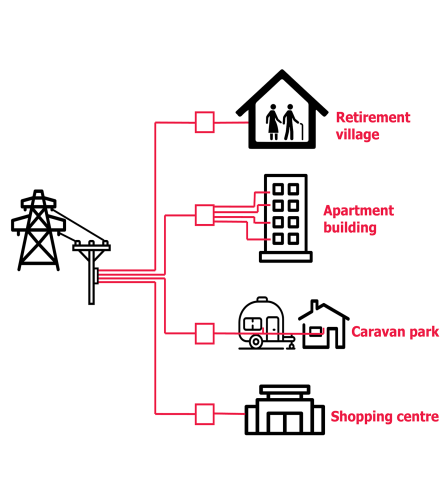
What is an exempt seller?
Some electricity sellers are exempt from requiring a retail licence. Generally exempt sellers buy electricity at a ‘gate’ meter, on selling it to individual customers.
Exempt sellers who sell electricity to residential and small business customers through an embedded network may include:
- apartment buildings
- caravan parks
- retirement villages
- shopping centres
- rooming houses.